What are the symptoms of a black widow spider bite?
What is a black widow spider?
Black widow spiders (Latrodectus mactans and Latrodectus hesperus) are found throughout southern Canada, the United States, and Mexico. A female black widow is much more likely to deliver more venom than a male spider. Female black widows are long-legged, shiny, coal-black spiders with an orange, red, or yellow shape on their underside that usually looks like an hourglass but may be another shape. Female black widows are usually about 3.8 cm (1.5 in.) long, but they may be smaller.
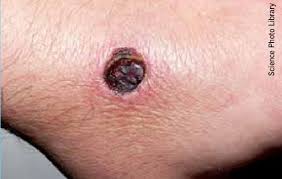
Black widow spiders are frequently found in low-lying webs in garages, in barbecue grills, around swimming pools, and in wood piles. Most bites occur in rural and suburban areas and occur between the months of April and October. These spiders tend to bite defensively when their webs are disturbed. Bites to babies, children, and older adults may be more serious.
What are the symptoms of a black widow spider bite?
In most cases of a black widow spider bite, symptoms consist only of:
Minimal to sharp pain followed by swelling and redness at the site of the bite.
One or two small fang marks like tiny red spots.
In some cases, severe symptoms appear within 30 to 60 minutes. These include:
Muscle cramps and spasms that start near the bite and then spread and increase in severity for 6 to 12 hours.
Seizures.
Chills, fever, nausea, or vomiting.
Sweating.
Severe belly, back, or chest pain.
Headache.
Stupor, restlessness, or shock.
Severe high blood pressure.
What should you do if you think you’ve been bitten by a black widow spider?
Follow these steps if you believe you have been bitten by a black widow spider.
Get medical help immediately.
Call your doctor, hospital, or local poison control centre.
Remain calm.
Too much excitement or movement will increase the flow of venom into the blood.
Apply ice to the bite area.
Do not apply a tourniquet.
It may cause more harm than benefit.
Try to positively identify the spider or catch it to confirm its type.
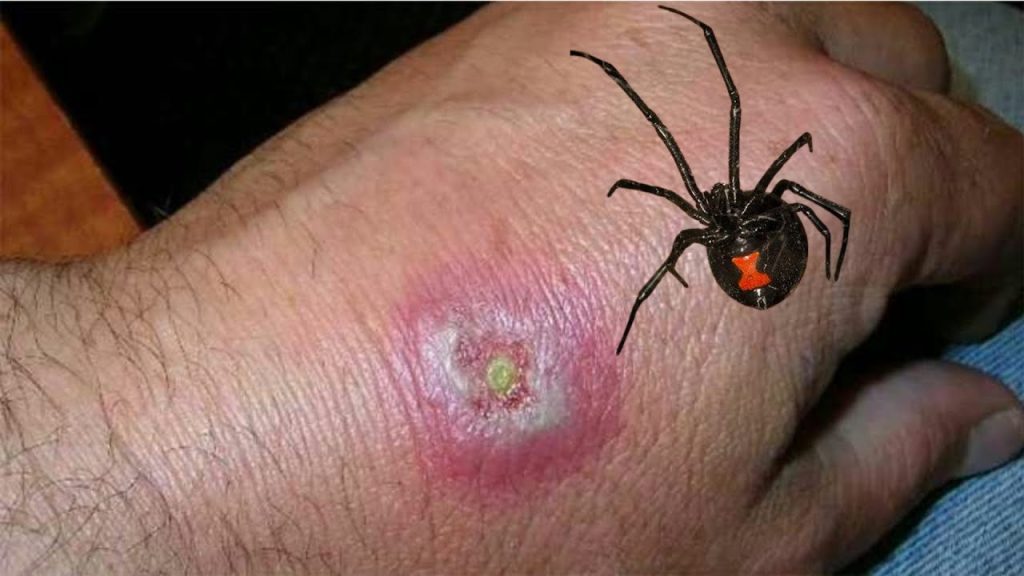
How is it diagnosed?
A black widow spider bite is diagnosed through a physical examination and questions about the bite. You should be prepared to describe the spider, where and when the bite took place, and what you were doing at the time. Your doctor will ask what your main symptoms are, when they began, and how they have developed, progressed, or changed since the bite.
How is a black widow spider bite treated?
Medicine to counteract black widow spider venom (antivenom) is available in Canada, the United States, and Mexico. It is usually used if you have trouble breathing, have high blood pressure, or are pregnant. Children and older adults with some medical conditions may also be given the medicine if their symptoms are serious.
Treatment also includes:
Medicine for pain and spasms. Pain and spasms may be severe enough to require benzodiazepines, such as lorazepam (Ativan) or diazepam (Valium), or opioids, such as morphine or fentanyl. Calcium may also be used.
Antihypertension medicines for high blood pressure.
Decoding the Black Widow Spider: Appearance, Habitat, and Venomous Bite

Photo byWikiImagesonPixabay
The black widow spider, a creature often wrapped in mystery and fear, has a reputation that precedes it. Known for its toxic bite and distinctive appearance, this spider is both intriguing and unnerving. This guide aims to demystify the black widow spider by providing a comprehensive overview of its appearance, habitat, and the symptoms and treatments associated with its bite.
Understanding the Black Widow Spider: An Overview
The black widow spider, belonging to the Latrodectus genus, is renowned for its venomous bite. It’s important to note that these spiders are not naturally aggressive and typically only bite humans when they feel threatened.
Species and Appearance
There are two species of black widow spiders that are predominant in the United States:
- The Southern Black Widow: This spider has a shiny black body, about a half-inch long, with a large, globe-shaped abdomen. The most recognizable feature is a red or orange hourglass-shaped mark on its underside.
- The Northern Black Widow: This variant has a row of red spots down the middle of the upper surface of its abdomen. It also has two crosswise bars on the underside. The markings, however, can also be yellow or white. The spider may be brown or have red legs.

Habitat
Black widow spiders are generally nocturnal, preferring cool, dark places like garages, sheds, and undisturbed corners of buildings. Outdoors, they are commonly found under decks, porches, and in woodpiles.
The Mark of the Black Widow: Bite Identification and Symptoms
Identifying a black widow spider bite is crucial for timely treatment. The bite of a black widow spider is distinguished by two faint red puncture spots at the site of the bite. However, with swelling and redness, the bite marks may not always be evident.
Symptoms of a Black Widow Spider Bite
The venom of a black widow spider affects the victim’s nervous system. The severity of the symptoms depends on the amount of venom injected and the individual’s sensitivity to the venom. Symptoms may appear within as little as 20 minutes and include the following:
- A raised, itchy bump or rash
- Pain at the site of the bite
- A red or purplish area of skin around the bite
- Blistering at the site of the bite
- Acute muscle pain and cramps, especially in the abdomen
- Nausea or vomiting
- Dizziness, chest pain, and respiratory difficulties in severe cases
- Elevated heart rate and blood pressure
Addressing the Bite of the Black Widow: Prevention and Treatment
Preventing a black widow spider bite involves awareness of their preferred habitats and avoiding disturbing them. Keeping storage areas clean and avoiding potential hiding spots such as woodpiles and fallen tree branches can reduce the risk of encounters.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Immediate medical attention should be sought if you suspect a black widow spider bite, especially if severe symptoms like widespread pain, fever, or nausea occur. It is particularly crucial for children and the elderly to seek immediate care as these bites can be fatal for them due to their smaller body sizes or weakened immune systems.
First Aid for Black Widow Spider Bites
While waiting for medical attention, the following first aid measures can be taken:
- Clean the bite site with soap and water
- Apply a cold compress or ice pack wrapped in cloth to the area
- Apply an antibiotic ointment to the site to prevent infection
- Elevate the bite site if it’s on an arm or leg to prevent swelling
- Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen can be used to manage pain
Medical Treatment for Black Widow Spider Bites
At the hospital, treatment may include antivenin injections, antibiotics, pain medications, and wound care. In extreme cases, doctors may administer antivenin, a drug made from substances in the blood of horses that neutralizes the black widow’s venom. Given the potential for side effects, this treatment requires close monitoring.

While the black widow spider’s bite can be dangerous, understanding its characteristics, habitat, and the symptoms associated with its bite can help prevent unfortunate encounters and ensure timely treatment. By being aware and taking necessary precautions, we can coexist with these fascinating creatures in our environment.
Remember, while most spider bites are harmless, the black widow’s bite requires immediate medical attention. Therefore, it’s always better to err on the side of caution and seek medical care if you suspect a black widow spider bite.
black widow spider
The Black Widow, (Latrodectus mactans), is a venomous spider of the family Theridiidae, order Araneida. The female, about 1.3 cm (0.5 in) long, is glossy black, densely clothed with microscopic hairs, and marked with a characteristic red hourglass on the underside of the abdomen. The male, which is rarely seen, is smaller than the female and has four pairs of red marks along the sides of the abdomen. The Black Widow is found in the warmer regions in every state in the United States except Alaska; it lives in a variety of natural and domestic habitats.
The life cycle of the widow spiders are all similar. The female lays approximately 250 eggs in an egg sac which is about 1/2 to 5/8 inch in diameter. The eggs hatch in 20 days and remain in the egg sac from about 4 days to 1 month.
The young spiders then molt to the second stage and begin feeding. As the young spiders grow, they construct a loosely woven web and capture progressively larger prey. Male spiders moult 3 to 6 times before maturing. The females moult 6 to 8 times and occasionally eat the males after mating. Generally, the females are not aggressive unless agitated, although they are prone to bite when guarding an egg sac.Help keep Spiderzrule going. Click to donate!
The venomous bite of the Black Widow Spider, causes muscle spasms and breathing difficulty in humans and may be fatal. The female is distinguished by a red hourglass marking on its underside. The diet of the Black Widow consists of insects, spiders, and centipedes captured with its web. After mating, the female may ensnare and feed upon her mate – hence the name Black Widow.
Here are some great photos of a black widow spider by Rich Swanner. All photos are copyright to their owners and may not be reproduced without permission.
