Probably the most notorious of all spiders, Sydney Funnel-webs have a fearsome reputation. Most of this is deserved, but some is exaggerated.
Identification
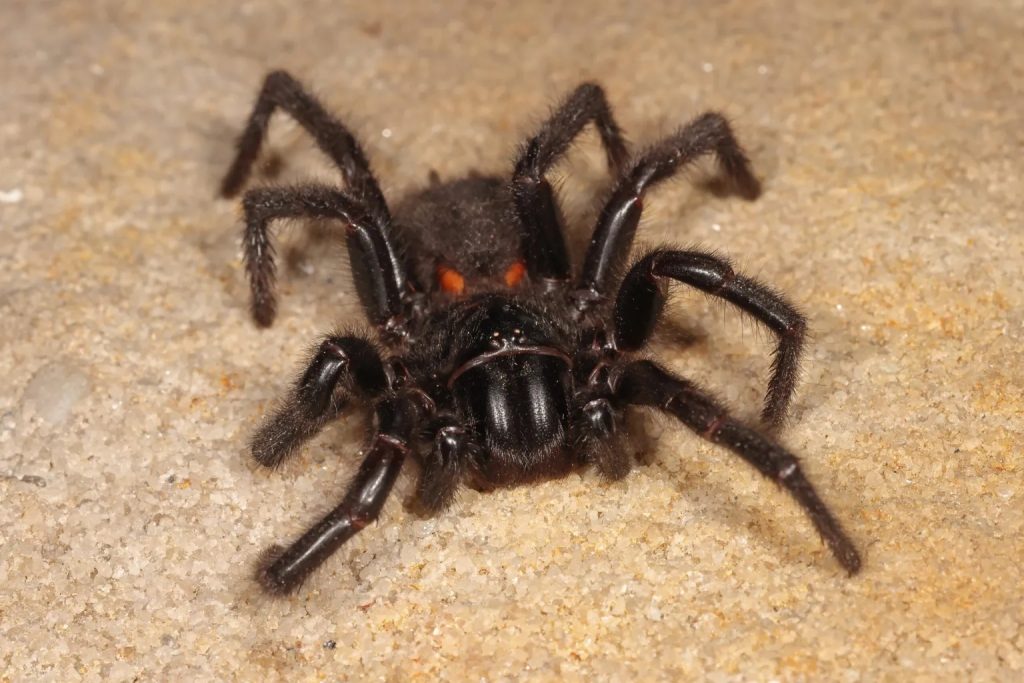
Sydney Funnel-webs are shiny, dark brown to black spiders with finger-like spinnerets (silk-spinning organs) at the end of their abdomen. Males have a large mating spur projecting from the middle of their second pair of legs. If threatened, Sydney Funnel-webs show aggressive behaviour, rearing and displaying their impressive fangs.

Distribution
The Sydney Funnel-web Spider (Atrax robustus) occurs in New South Wales, from Newcastle to Nowra and west to Lithgow. They especially favour the forested upland areas surrounding the lower, more open country of the central Cumberland Basin. This includes the Hornsby Plateau to the north, the foothills of the Blue Mountains to the west, and the Woronora Plateau to the south. Funnel-web occurrence is low in much of central-western Sydney, and also the sandy coastal parts of the eastern suburbs and the Botany Bay area. They do better in areas of sandy clay, shale or basaltic soils that can retain moisture more effectively.
What happens if you get bitten by a Sydney funnel-web spider?
Funnel-web spider bites can be life threatening, especially in children. They must be treated quickly with antivenin by an experienced provider. Even with appropriate and quick treatment, symptoms may last for several days to weeks. The original bite may be small and may progress to a blood blister and look like a bull’s eye. (This is similar to the appearance of a brown recluse spider bite.)
The area affected by the bite may become deeper. Additional symptoms such as fever, chills, and other signs of additional organ system involvement may develop. Deep scarring may occur and surgery may be needed to improve appearance of the scar.
Is the Sydney funnel-web spider the deadliest spider?
Although they are one of the most venomous species of spider in the world, there have been no fatalities from Sydney Funnel-web Spider bites since the introduction of antivenom.
How painful is a Sydney funnel-web spider bite?
If envenomation has occurred, the bite site may be extremely painful, although tissue necrosis is not seen. There is some evidence that prolonged immobilisation of venom in the tissues may lead to inactivation. Symptoms can develop within minutes if effective first aid is not employed.
What is the difference between a Sydney funnel-web spider and a black widow?
Behaviorally, Funnel-web spiders are more dangerous than black widows or brown recluses because they become aggressive when threatened. If you tried to shoo one away, it’s less likely to skitter off.
What is the number 1 deadliest spider in the world?
Funnel-web spiders top the list of deadliest spiders, if only for their storied venom. Native to Australia, these spiders boast venom that’s so potent their bite can kill within minutes. “The deadliest is probably the funnel-web spider and its relatives.
SYDNEY (AP) — With fangs that could pierce a human fingernail, the largest male specimen of the world’s most venomous arachnid has found a new home at the Australian Reptile Park where it will help save lives after a member of the public discovered it by chance.
The deadly Sydney funnel-web spider dubbed “Hercules” was found on the Central Coast, about 50 miles north of Sydney, and was initially given to a local hospital, the Australian Reptile Park said in a statement Thursday.
Spider experts from the nearby park retrieved it and soon realized it was the largest male specimen ever received from the public in Australia.
The spider measured 7.9 centimeters (3.1 inches) from foot to foot, surpassing the park’s previous record-holder from 2018, the male funnel-web named “Colossus”.
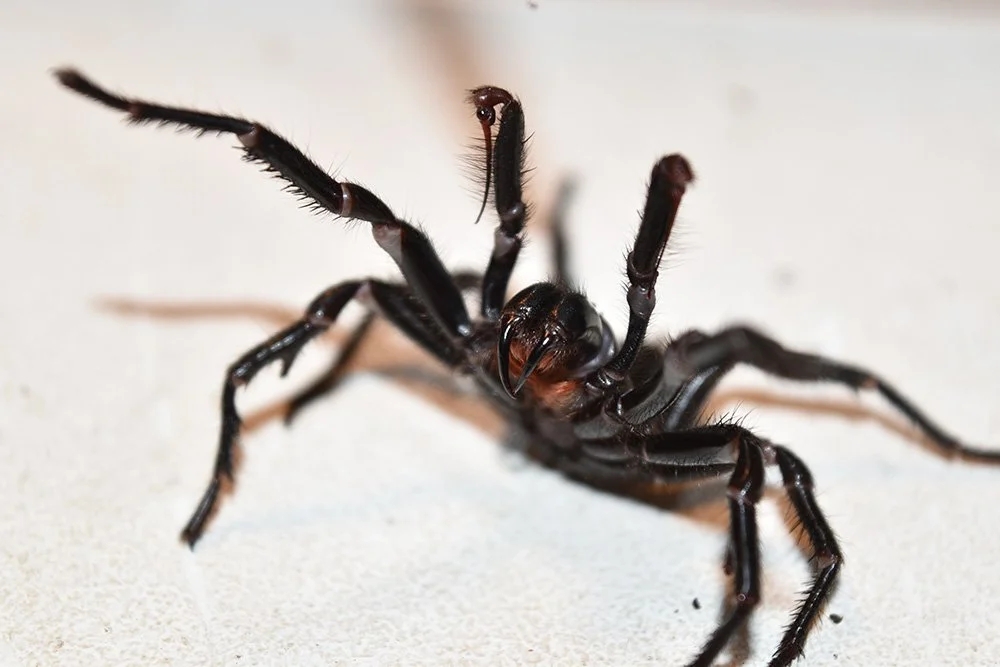

“Whilst female funnel-web spiders are venomous, males have proven to be more lethal. With having a male funnel-web this size in our collection, his venom output could be enormous, proving incredibly valuable for the park’s venom program.”
Female Funnel web spider (Photo David McClenaghan, CSIRO Entomology)
There are several species of funnel web spider (Atrax robustus and Hadronyche sp.) found throughout Australia. The best known of these is the Sydney funnel web spider, Atrax robustus. The male of this species is one of Australia’s most dangerous spiders, and is thought to have been responsible for all 13 recorded deaths. While capable of causing death in as little as 15 minutes, no deaths have been recorded since the development of the antivenom in the early 1980s.
There are several species of funnel web spider found throughout Australia. The best known of these is the Sydney funnel web spider, Atrax robustus. The male of this species (in the picture on the left) is Australia’s most dangerous spider, and is capable of causing death in as little as 15 minutes. The Sydney funnel web is a large, black aggressive spider with large powerful fangs. It lives in burrows or crevices in rocks or around house foundations, lining the burrows with silk. Colonies of more than 100 spiders may be found. The male spiders in particular tend to wander into houses in the summer, especially in wet weather. It is unusual amongst spiders in that the male appears to be more dangerous than the female. It is also of note that the venom appears to particularly affect primates, whereas other mammals are relatively resistant.
Several other funnel web spiders species have been described throughout Australia, including the northern or tree-dwelling funnel web (Hadronyche formidabilis), found in northern New South Wales and southern Queensland, as well as species found in Victoria, South Australia and Tasmania .
Funnel web Spider bite in Australia
Prior to the development of the Sydney funnel web antivenom in 19801 and it’s clinical introduction in 19812, there had been 13 known fatalities associated with bites from this spider. Since the antivenom has been in use, no deaths have been recorded, and time spent by bite victims in hospital has been greatly reduced. Most bites occur in the warmer months, and are predominantly sustained on the extremities. The pressure immobilisation method of first aid should be employed for bites by any large black spider in the Sydney area, since the illness caused by funnel web bites may be rapidly progressive and death may ensue within minutes to hours. Children are especially at risk, due to their lower body weight and the potential for multiple bites to occur if the spiders are handled.
